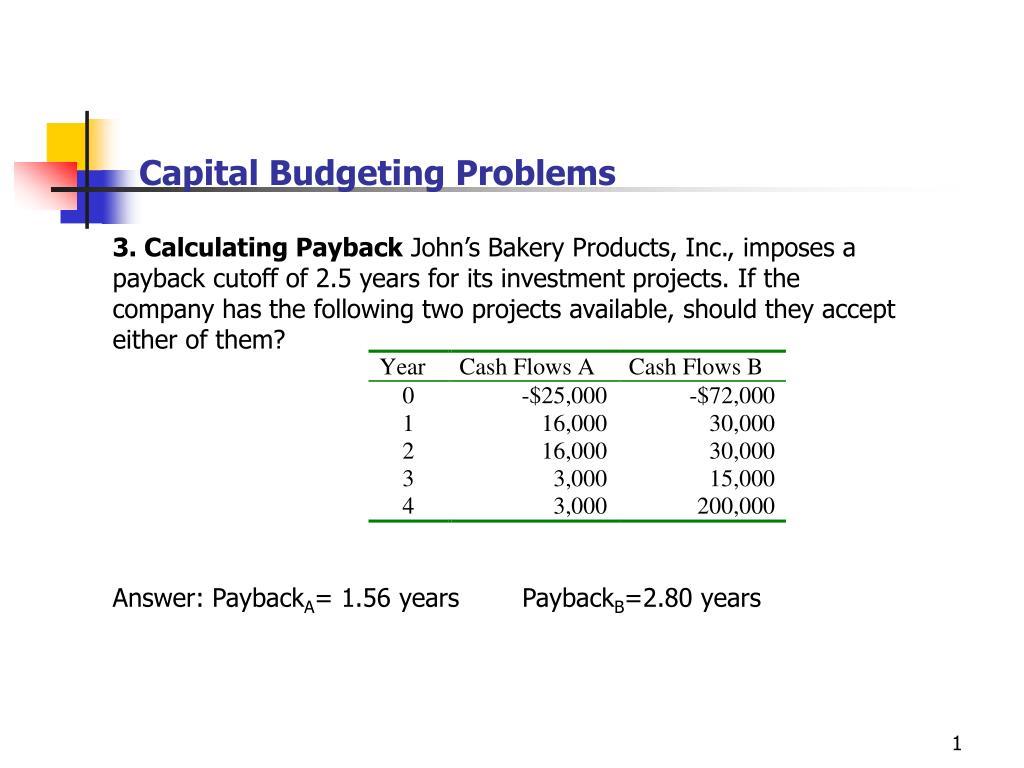
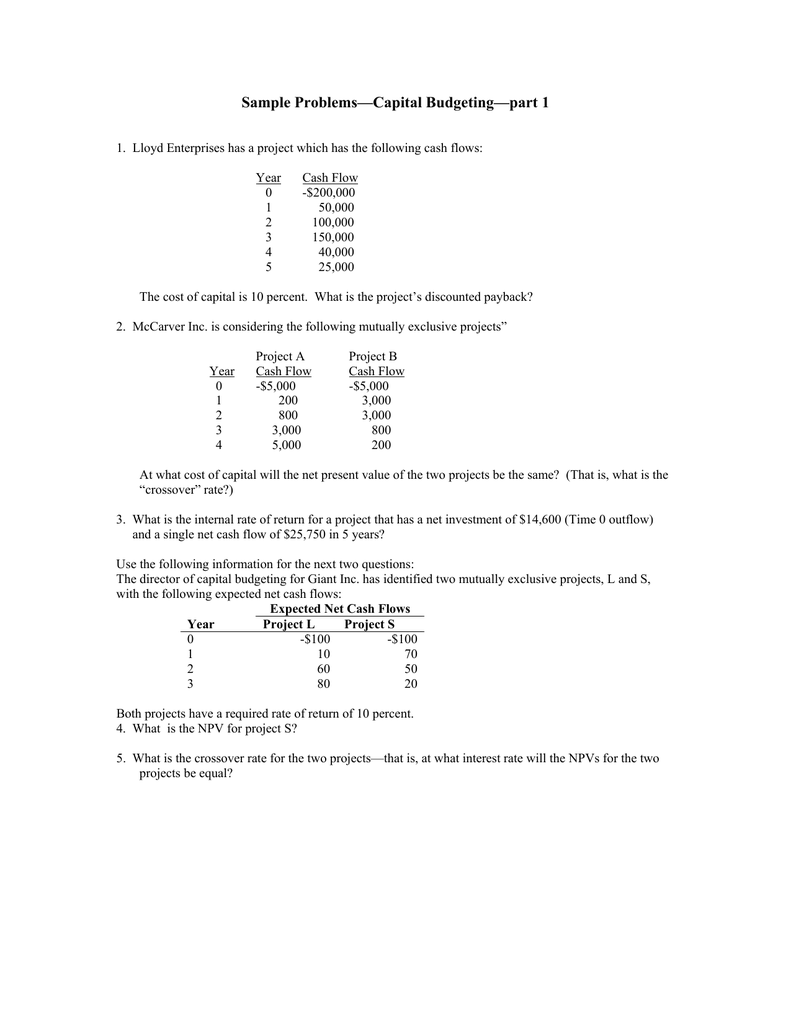
Poor capital budgeting decisions can destroy wealth almost as quickly (especially if the firm does not recognize failure quickly enough and continues to throw good money after bad). While we will focus only on a small portion of the process (making the decision), it is worthwhile to look at the process as a whole. As we have discussed since chapter one, investors are risk averse.
Post Payback Profitability Method
NPV is calculated by estimating a company’s future cash flows related to a project. Then, these cash flows are discounted to present value using a discount rate representing the project’s capital costs, risk, and desired rate of return. The sum of all discounted cash flows represents the net present value, and the net present value is the difference between the project cost and the income it generates over time. In conclusion, capital budgeting is crucial for businesses that plan to invest in new projects. This process uses finance methods, such as Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR), to pick the best projects.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
- The objective of capital budgeting is to rank the various investment opportunities according to the expected earnings they will yield.
- The useful life for the Diamond LX and VIP Express models are 12 and 10 years, respectively.
- Net present value describes as the summation of the present value of cash inflow and the present value of cash outflow.
- Flexibility is the capacity to adjust the scale, scope, timing, and execution of the projects in response to new information and uncertainties.
There is every possibility that shareholders will derive the maximum benefit, which in turn results in wealth maximization. As mentioned earlier, these are long-term and substantial capital investments, which are made with the intention of increasing profits in the coming years. In particular, the amount invested in fixed assets should ideally not be locked up in capital goods, which may have a far-reaching effect on the success or failure of an enterprise. Thus, it is a process of deciding whether or not to commit resources to a project whose benefit would be spread over the years.
Techniques/Methods of Capital Budgeting
Project B cost $1000 and will return $1500 at the end of 1 year. The first project has a 100% IRR while the second project only has a 50% IRR. However, if you could only take one of these two projects, which would be better? Clearly Project B is a better choice in that you will make $500 beyond your initial investment. If you took Project A, while you earned a higher return you would only make enough profit to visit the $1 menu at your local fast-food chain.
What are the five methods of capital budgeting?
Based on our findings, we can then recommend the capital budgeting technique to use. NPV profile is a graph that shows the relationship between a project’s NPV and the required return on the project. To draw the NPV profile, we first need the project’s NPV at a number of different discount rates. Let’s stick with the example above, which requires an initial investment of $2,000 and generates $900 per year for the next three years.
Investments lead to being unable to utilize assets or overutilization of fixed assets. Therefore, before making the investment, it is required careful planning and analysis of the project thoroughly. The capital investment decisions are irreversible and are not changed back.
The primary reason to implement capital budgeting is to achieve forecasting revenue a project may possibly generate. All the upfront costs or the future revenue are all only estimates at this point. An overestimation or an underestimation could ultimately be detrimental to the performance of the business. While companies would like to take up all the projects that maximize the benefits of the shareholders, they also understand that there is a limitation on the money that they can employ for those projects. Therefore, they utilize capital budgeting strategies to assess which initiatives will provide the best returns across a given period. Owing to its culpability and quantifying abilities, capital budgeting is a preferred way of establishing if a project will yield results.
This method provides the ratio of the present value of future cash inflows to the initial investment. A Profitability Index that presents a value lower than 1.0 is indicative of lower cash inflows than the initial cost of investment. Aligned with this, a profitability index great than 1.0 presents better cash inflows and therefore, the small business general ledger accounts examples and more project will be accepted. The process focuses on future cash flows rather than past expenses. Some of the major advantages of the NPV approach include its overall usefulness and that the NPV provides a direct measure of added profitability. There are drawbacks to using the payback metric to determine capital budgeting decisions.